...
| Expand |
|---|
| title | I forgot my username/ password. What should I do now? |
|---|
|
| Your username will be your registered email address, however, if you have forgotten it please contact the WMDA office by email support@wmda.info. If you have forgotten your password, click on the 'Forgot Your Password' link, enter your email address and click on 'Send Password Reset Link' (feature not yet available. Will be added soon). You will then receive an email with a link to follow - click on the link and reset your password. Please notice you must use the link within 30 mins, otherwise, you will trigger an error page "Sorry, an error has occurred". |
...
PATIENT MANAGEMENT
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How can I quickly access the details of a patient within WMDA? |
|---|
|
Patient information can be accessed from the 'Patient List' by selecting the "Patient ID'. The patient information can also be accessed from the Patient's Match Result List by opening the 'Patient Details' box and selecting the 'Edit Patient' button. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why can I not find a particular patient? |
|---|
|
Patients for whom a search was performed within the last month will be in the ‘Active patient’ list, while the previous 5 months will be in the ‘Inactive patient’ list. If you cannot find your patient within the default Active list remember to search the Inactive list also. Users will have access to patients registered by other users at their organisation as well, which is also split into 'Active Patients' and 'Inactive patients' |
| Will my patients from the legacy system (v1) be available in the new system? |
|
No. Because of the way the two systems are built they do not share the same database. Therefore patients from V1 will not be available in V2 by default. If you'd still like to have your V1 patients visible in the V2 system, there are three ways to achieve this: - You implement the patient API endpoints for the V2 system and use it to send over the patients in V1 to V2. This could also be just the relevant patients. You could then keep using the patient API V2 implementation to send patients from your local system to Search & Match V2.
- You provide us with a list of requirements for patients in your V1 system and we will port them over to the new system. The WMDA will only do this once for an organisation.
- You manually enter the relevant patients from the V1 system into the V2 system.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How can I quickly access the details of a patient within WMDA? |
|---|
|
Patient information can be accessed from the 'Patient List' by selecting the "Patient ID'. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why can I not find a particular patient? |
|---|
|
Patients for whom a search was performed within the last 6 weeks will be in the ‘Active patient’ list, while the previous 5 months will be in the ‘Inactive patient’ list. If you cannot find your patient within the default Active list remember to search the Inactive list also. Users will have access to patients registered by other users at their organisation as well, which is also split into 'Active Patients' and 'Inactive patients' |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | I have a large list of patients. How can I easily find my patient? |
|---|
|
There are different tools in the patient list to search or sort your list which will make it easier to find your patient: Use the Search by patient ID box when you know the patient ID or part of it.You can sort the list on every column (except from the results column), so you can for example sort on birth date and then find your patient.When you are looking for a patient not entered by yourself, you can sort on username at the view with all patients from your organisation. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Does De-activating a patient record delete it from the system? |
|---|
|
No. De-activating a patient will just remove it the searches and search results from the Hap-E Search and ATLAS server and the 'Active patients' list and place it patient and place the patient in the 'Inactive patients' list. |
...
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How is the patient list sorted by default? |
|---|
|
The patients in the patient list are default sorted on the date of last viewed. The records that have not been viewed at all are placed at the top, followed by the most recently viewed record.Records that have been created are also considered to have been "viewed" and there will therefore appear at the top after creation. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | When I switch between views (just my patient vs all patients from my organisation) at the Inactive patient list, I am referred back to the Active patient list. How can I switch between views in the Inactive patient list? |
|---|
|
The easiest way is to change the view first in your "Active" patient list and then go to the Inactive patient list. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Does the system auto correct HLA? |
|---|
|
No, the system does not auto correct HLA information, but may give you error warnings as applicable. |
SEARCHING
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is the difference between urgent and non urgent patients? |
|---|
|
Urgent and Non-Urgent indicators on patients are a tool for you to use to prioritise your patient searches. At this time, the Search and Match Service does not use this information and will not affect the speed of your match run. |
SEARCHING
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is asynchronous matching? |
|---|
|
Asynchronous matching is a process of running searches in parallel. It allows you to enter a patient and start the search run, and proceed with other activities within the application like entering another patient or reviewing another match list while the search runs in the background. The user does not have to wait for the current search to finish before proceeding with other activities. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why do some search requests take long to retrieve? |
|---|
|
Many factors can impact how long it takes to retrieve search results. The most likely reasons that your search is taking some time is that it is a difficult search or the HLA of your patient is very common and will retrieve many records. We initially only run a 10/10, 8/8 or 6/6 search to make sure we retrieve you results as quickly as possible. Mismatch searches can take longer since there are many more options to assess before providing the results. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Can I cancel a search if it’s taking too long? |
|---|
|
| It is not necessary to cancel a search. We recommend logging out of the application and returning at a later time to review your results. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Which match types are used for the initial donor/cord match run? |
|---|
|
The system by default runs for donors a 10/10 match run using the haplotype frequency algorithm if all 5 loci (A,B,C,DRB1,DQB1) are available for the patient. If only 3 or 4 loci are available, the system will scale down to respectively a 6/6 or 8/8 match run. 10/10, 8/8 and 6/6 are all considered as zero mismatch runs and will not include mismatch donors in the results. The system by default runs for cords a ≥8/10 match run at allele level using the haplotype frequency algorithm. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What does Run Mismatch search mean? |
|---|
|
By default, the Search & Match Service only provides 10/10, 8/8 or 6/6 matches initially. Selecting the 'Run Mismatch' search button allows you to request a mismatch search to review e.g. 9/10 or 7/8 match results. Once those results return, you will be able to review them by specific loci mismatches or any loci. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Is it possible to run a mismatch run at the first initial match run? |
|---|
|
No, at this moment you can only run a zero mismatch donor and/or ≥8/10 cords run as a first match run. You have to requested the mismatch donor run after you retrieved the zero mismatch run results. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is the difference between Allele and Haplotype frequencies? |
|---|
|
Allele frequencies give the proportions of individual alleles. Haplotype frequencies give the proportions of specific haplotypes i.e. several alleles in phase and therefore preserve linkage information. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What Haplotype Frequencies will be used for the probability matching? |
|---|
|
| The Search & Match Service uses a Global Frequency set determined from the comprehensive donor file. Read more on the following page. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Can I switch off the Predictive Search and run it just like the old system? |
|---|
|
| You can switch to use allele frequencies instead of haplotype frequencies, which is the matching approach/method that the old system used. However, all matching algorithms vary slightly so the new search powered by Hap-E Search and/or ATLAS may not match results from the old system, even with allele frequencies in use. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How can I request a Search Advise for a Patient? |
|---|
|
If you are experiencing difficulties in your selection of a donor/cord for your patient, you can request a search advice from the WMDA HLA experts. To request an advise, go to your patient list, click on the patient ID and at the bottom of the Update patient form you will find a button with 'Request Search Advisory'. An email message will then open with the patient information and some additional fields with requirements. Please fill out as much as possible and send the email. You will receive the advice also by email. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is the difference between setting filters and heading/on-screen filters within the search results report? |
|---|
|
Setting the filters in the 'Search Settings' on the Search results page prompts a new search request with those parameters. These filters will also not influence the number of results you will retrieve and will be saved in your search results. The heading/ on-screen filters on the match results table will filter and reduce the results list that is already available. Donors and cords will retain their row number from the original list without any on-screen filters applied. The on-screen filters will not be saved to your search results and when you leave the search results page the on-screen filters will no longer be there when you come back. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Are changes to the search report settings reset by the system? |
|---|
|
Only changes applied from the search setting box will be saved to your search results. Any other on-screen filters or flags won't be saved and are reset by the system when you leave the search results page. |
...
| title | It seems like the search results are automatically ordered on age for adults and TNC for cords. Is that correct? |
|---|
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS for donors are:
1. HLA
2. probability in 10% intervals
3. donor age in 5 year intervals for adults
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS for cords are:
1. HLA (6/6, 5/6, 4/6 categories)
2. Number of total nucleated cells (TNC) for cords within HLA match category
...
| title | What are the DBP1 TC3 evaluvation conditions |
|---|
DPB1 TCE3 evaluation is performed only for A-B-DR(B1) typed donors under the following conditions:
- Patient DPB1 values must be present. Typing ambiguities in the form of multiple alleles codes, G-codes, etc. are allowed.
- Donor DPB1 values must be present. Typing ambiguities in the form of multiple alleles codes, G-codes, etc. are allowed.
- The donor must be in the group of potential "9/10" and "10/10" identical donors. Therefore, it is implicitly assumed that a 5-locus search report is retrieved and can be accessed. In case of a 4- or 3-locus search reports or deactivation of the grouping by allele differences, there will be no TCE3 grading.
| Why are not all donors shown? |
|
Hap-E searches may return donors that do not have typing at DRB1, but do have typing at loci A, B and at least one other locus. Since these donors are usually not considered relevant potential donors and there tend to be quite a few of these donors that potentially match the patient, Search & Match applies a default filter which removes all donors that do not have typing at DRB1. You can see this by the little "1" next to the filter.  Image Added Image Added
This means that there is already a filter applied to the results. If you are interested in the donors without DRB1 typing you can remove the filter and see all results.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why are certain search results returned that seem to be an obvious mismatch? |
|---|
|
If this occurs the most likely cause is: - Your patient has homozygous typing at at least 1 locus
- The potential donor/CBU has low resolution typing at this locus or a MAC code that contains a null allele
The reason this donor/CBU is shown as a potential match and not a mismatch is that the typing for the donor contains a null allele. It is therefore a possibility that the donor actually has a null allele. Since a homozygous typing is generally considered a match with a donor that has one allele that matches the homozygous patient typing and the other is a null allele, Hap-E returns this donor/CBU as a potential match. Please see the slide below from a recent webinar:
 Image Added Image Added
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why is the number of search results so different than in the legacy system? |
|---|
|
In the legacy system when running a standard donor search, all returned donors have values for A, B and DRB1. This is different when running a search in the new system. There all donors need to have typing at A, B and at least one other locus (which may or may not be DRB1). This means that donors are returned in the new system that do not have typing at DRB1. This typically explains the majority of the difference in number of search results as mentioned in the search summary.
Although in some cases these donors with typing at A, B and C or DQB1 may prove useful, in most cases they are not. We therefore apply a default filter to all search results. You can see all donors by unchecking the default filter.  Image Added Image Added
Because the filter is applied by default, you may notice a difference in the total number of donors/cords as described in the search summary text versus the number displayed just above the list of potential matches. For example in the example below, there are 33 donors in the full search results. 3 donors did not have typing at DRB1 and have therefore been filtered out in the donor search results shown. You can see that a filter has been applied by the "1" icon on the "All filters" button.  Image Added Image Added
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is asynchronous matching? |
|---|
|
Asynchronous matching is a process of running searches in parallel. It allows you to enter a patient and start the search run, and proceed with other activities within the application like entering another patient or reviewing another match list while the search runs in the background. You do not have to wait for the current search to finish before proceeding with other activities. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why do some search requests take long to retrieve? |
|---|
|
Many factors can impact how long it takes to retrieve search results. The most likely reasons that your search is taking some time is that it is a difficult search or the HLA of your patient is very common and will retrieve many records. We initially only run a 10/10, 8/8 or 6/6 search to make sure we retrieve you results as quickly as possible. Mismatch searches can take longer since there are many more options to assess before providing the results. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What are inexplicable donors? |
|---|
|
Inexplicable donors or CBUs are records that have HLA that cannot be explained by a combination of two haplotypes in the haplotype frequency (HF) set for the population that the donor or CBU is part of. Because the HLA typing of this donor/CBU cannot be explained, the matching algorithm is unable to calculate match probabilities. Currently these donors appear on the bottom of the match class that they are part of (e.g. 10/10, 9/10, 7/8). The number of inexplicable donors/CBUs mentioned therefore serves as a reminder that there are potentially relevant search results available that can be found at the bottom of the match class. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Can I cancel a search if it’s taking too long? |
|---|
|
| It is not necessary to cancel a search. We recommend logging out of the application and returning at a later time to review your results. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Which match types are used for the initial donor/cord search? |
|---|
|
By default, Search & Match performs a 10/10 search for donors if all 5 loci (A,B,C,DRB1,DQB1) are available for the patient. If only 3 or 4 loci are available, the system will scale down to a 6/6 or 8/8 search, respectively. 10/10, 8/8 and 6/6 are all considered as zero mismatch searches and will not include mismatch donors in the results. This is also the case for cord searches. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How do I perform a search for mismatched donors? |
|---|
|
Open up the search results for a search you would like to perform a mismatch search. Click "Edit search" and then select the number of mismatches that you would like to consider at most. Then click "Search" to start that search. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Is it possible to perform a search for mismatched donors during the initial search? |
|---|
|
No, you can only perform a zero mismatch donor or cords search. You will only be able to view/request mismatched donors/CBUs when the initial search results are available. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What Haplotype Frequencies will be used for the probability matching? |
|---|
|
| WMDA has calculated and applied many specific haplotype frequency sets to the Search & Match Service. Read more on the following page. To find which haplotype frequency set got used for a donor or CBU, consult the full report. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How can I request a Search Advise for a Patient? |
|---|
|
If you are experiencing difficulties in your selection of a donor/cord for your patient, you can request a search advice from the WMDA HLA experts. To request an advise, go to your patient list, click on the patient ID and at the bottom of the Update patient form you will find a button with 'Request Search Advisory'. An email message will then open with the patient information and some additional fields with requirements. Please fill out as much as possible and send the email. You will receive the advice also by email. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What is the difference between setting filters and heading filters within the search results report? |
|---|
|
There is no functional difference. The filters you see on top of the headings in the search results are the frequently used filters. All filters are applied to all search results. Even the ones that are not on the page that is currently displayed. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | It seems like the search results are automatically ordered on age for adults and TNC for cords. Is that correct? |
|---|
|
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS for donors are: 1. HLA 2. probability in 10% intervals 3. donor age ascending
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS for cords are: 1. HLA (6/6, 5/6, 4/6 categories) 2. Number of total nucleated cells (TNC) for cords within HLA match category |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What are the DBP1 TC3 evaluation conditions |
|---|
|
DPB1 TCE3 evaluation is performed only for A-B-DR(B1) typed donors under the following conditions: - Patient DPB1 values must be present. Typing ambiguities in the form of multiple alleles codes, G-codes, etc. are allowed.
- Donor DPB1 values must be present. Typing ambiguities in the form of multiple alleles codes, G-codes, etc. are allowed.
As part of the DPB1 TC3 grading filter, you can filter the results by the following options: Matched, Permissive, Non-permissive in HvG direction, Non-permissive in GvH direction, Ambiguous/Undetermined. Although the DPB1 TC3 filter is available for cords, the results haven't been validated so it shouldn't be used.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What sequence do donors appear in on the reports? Are any types of donors given precedence? |
|---|
|
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS are: 1. HLA 2. probability in 10% intervals 3. donor age in 5 year intervals |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why are there sometimes probabilities missing? |
|---|
|
This can have several causes. - Overall match probabilities and locus-specific match probabilities are missing: this is most likely because the HLA typing of the donor/CBU is not consistent with any known haplotypes for the population that the donor is in (inexplicable donor). Without haplotypical context, the matching engine is not able to provide match probabilities.
- Only locus-specific match probabilities are missing: It does not make sense to display the probability of match for a specific locus in case of a mismatch
- Because the known match probability is 100% and therefore there is no probability of a(n additional) mismatch and therefore displaying match probabilities in case of an additional mismatch does not make sense.
- Because the probability of an additional mismatch is 0% for another reason, e.g. because the donor is low resolution typed at 3 loci and therefore in theory be a match, but it is very unlikely.
See the following page for more information: Feature differences Hap-E Search vs Optimatch |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why do i sometimes see donors or CBUs with no information other than HLA and Ethnicity? |
|---|
|
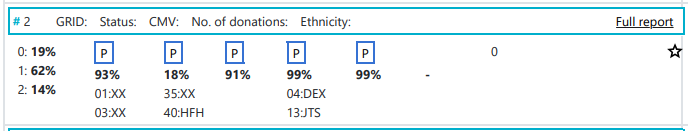 Image Added Image Added
In some cases you may see donors or CBUs that look like the one above. There is not information regarding GRID, registry, CBB, age or any other non-HLA/ethnicity information. The reason for this is that the search was in the Hap-E search result, but can no longer be found in our internal database. We are therefore not able to show any additional information other then what the Hap-E matching engine provided. This can have several causes. - The search was not recently performed and the patient is not in the ACT state.
- It is a donor from the Japanese registry (ION-4364). In that case there is registry information available, but all donors seem to be 33 years old and there are no identifiers. This is because Japan Marrow Donor Program does not send any information except for HLA to our systems.
- It is a donor from the Chinese Marrow Donor Program (ION-2197). In that case there is registry information available, but all donors seem to be 33 years old and there is no GRID. This is because Chinese Marrow Donor Program did not send GRID or birth date in their last upload (2017-11-09)
How to resolve: - If the search is not recent, it is best to refresh the searches for a patient. See https://share.wmda.info/x/dZUZGQ for instructions on how to do that.
- If the donor is from the Japan Marrow Donor Program or Chinese Marrow Donor Program, contact this registry for more information.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What are inexplicable donors/CBUs? |
|---|
|
At the top of search results you can see how many donors or CBUs are inexplicable.
 Image Added Image Added Inexplicable donors or CBUs are records that have HLA that cannot be explained by a combination of two haplotypes in the haplotype frequency set (Haplotype frequency sets in the HAP-E matching algorithm of the Search & Match Service) for the population that the donor or CBU is part of. To find out which haplotype frequency set was used, you can use the full report 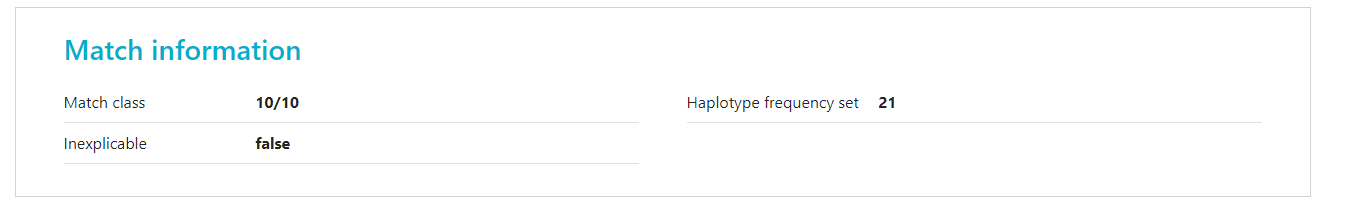 Image Added Image Added
The number there corresponds to the set on the Haplotype frequency sets in the HAP-E matching algorithm of the Search & Match Service share page. Because the HLA typing that this donor/CBU has cannot be explained, Hap-E also cannot calculate match probabilities. Currently these donors appear on the bottom of the match class that they are part of (e.g. 10/10, 9/10, 7/8). We are working on a way to move potentially relevant but inexplicable donors to a better place in the search results. The number of inexplicable donors/CBUs mentioned therefore serves as a reminder that there are potentially relevant search results available that can be found at the bottom of the match class. |
As part of the DPB1 TC3 grading filter, you can filter the results by the following options: Permissive, Non-permissive in HvG direction, Non-permissive in GvH direction, Ambiguous, Unknown.
Although the DPB1 TC3 filter is available for cords, the results haven't been validated so it shouldn't be used.
| Expand |
|---|
| title | What sequence do donors appear in on the reports? Are any types of donors given precedence? |
|---|
|
The default sorting criteria from Hap-E Search and ATLAS are: 1. HLA 2. probability in 10% intervals 3. donor age in 5 year intervals |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | The cords results in the former BMDW were displayed according 6/6, 5/6, 4/6 or less. Is that also in this system? |
|---|
|
Yes, all cords are sorted based on out of 6 HLA matching and TNC. So on top of your results you will find potential 6/6 matched cords with the largest unit (based on TNC) one on top of the page, followed by the 5/6 cords and 4/6 cords (depending on the match type you selected). |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | I would like to sort a haplotype frequency-based search report according to HLA-C. Is that possible? |
|---|
|
It is not possible to sort the search results in the match results table. You do have the ability to use many filters and to use different match types. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why are there sometimes probabilities missing? |
|---|
|
These donors don't have haplotype probabilities. This is usually the case when the phenotype could not be explained with the haplotypes given in the frequency set (inexplicable donor). Without haplotypical context, the programme gives only allele frequencies for the tested loci. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why is, for example, a donor with B*15:BPXE not shown as a potential match for a patient with B*15:03? And why was such a donor shown in the “old BMDW”03? |
|---|
|
Part 1: Since B*15:BPXE = B*15:03/61/74/103 a donor with this codes is a potential allele match for the patient. According to the official WMDA serology/DNA correspondence table, B*15:61 and B*15:74 have a serology of B15/B70 while B*15:03 is B72 and B*15:103 is B70. As a consequence a serology of B15 rules out B*15:03 and this donor is no longer potentially identical (on the allele level). Another explanation could be the limited length of donor lists.Part 2: In the old BMDW serology was ignored when DNA typing was available so B*15:03 was not excluded. The new system does not modify or ignore donor data and respects and relies on the responsibility of the providing registry for its data15:03 and this donor is no longer potentially identical (on the allele level). Another explanation could be the limited length of donor lists. Background: Unfortunately, for many donors serology was derived from DNA (by using the first field for the serological assignment) and vice versa (by appending “:XX” to the serological assignment) and often eventually both values are reported. In the case discussed, B*15:BPXE probably was translated back into B15 which is most likely wrong. This is a typical and (with certain registries) frequent case but there are many more unexpected DNA-serology correspondences that can give rise to exactly the same situation. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why is a male donor listed after a female donor of the same age and HLA? Why is a donor with an identical CMV status listed after one with a missing or different CMV status? |
|---|
|
Hap-E Search and ATLAS Match does not consider binary attributes like gender or CMV for sorting sorting at all. If you see a rich donor list and prefer, for example, male male donors you should use the filtering capability of the algorithmsapply the filter to see male donors only. Rationale: There is no agreed concept for weighing secondary match criteria criteria like age, gender or CMV against each other. The approach to sort by probability in blocks and then by age plus ad hoc filtering gives the user maximum control of the appearance of the list. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why is a matching donor who is typed at higher resolution listed after donors typed at lower resolution? |
|---|
|
This can happen only if the difference in resolution is not considered considered sufficiently relevant in the given context by Hap-E Search and ATLAS. Below are some possible (not mutually exclusive) reasons: - The allele designations encode for the identical ARD (antigen recognition domainAntigen Recognition Domain) and Hap-E Search and ATLAS only matches for the ARD part of the HLA protein complex. For example B*07:ANVB stands for B*07:02/07:61 which both encode for the same ARD (here: exon 2 and 3). Hence Hap-E Search and ATLAS is regarding the codes B*07:02, B*07:61 and B*07:ANVB all as allele matches for each other but might give different matching probabilities for phenotypes containing each of those three codes since haplotypes involving B*07:02 and B*07:61 are having individual frequencies.of those three codes since haplotypes involving B*07:02 and B*07:61 are having individual frequencies.
- The resolution only looks higher but, in fact, is lower The resolution only looks higher but, in fact, is lower (e.g. B*15:12 currently is only a single allele while B*15:12:01G covers three), identical (e.g. A*80:01, A*80:01:01 and A*80:01:01G cover exactly the same alleles) or not directly comparable since each code is containing some alleles not covered by the other (e.g. comparing B*07:TDVB and 15:14 currently is only a single allele while B*0715:02:01G the former also covers a lot more variants of B*07:02 like B*07:02:02 to B*07:02:05 while it is excluding other alleles like B*07:44 and B*07:49N).
- The broader code only contains additional alleles which have never been observed in the population whose haplotype frequencies are used - at least not in a relevant haplotypical context. Their frequency could also be so low that it is disregarded due to rounding or the 10% probability grouping explained elsewhere. This applies, in particular, to all null variants of expressed alleles with identical first two field designations.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why do I see two alleles in bold on a locus in the one mismatch(9/10) category? |
|---|
|
In rare cases the match program cannot decide which of two B locus results are a mismatch, in those cases both are given in bold. For example, the patient is B*27:05, 44:03; the donor is B*44:ABYM, 44*AFFK. In this case both multiple allele codes include 44:03 therefore the match program cannot choose between them. See example image below where donor 12 on the search report is being marked as having two HLA-B mismatches, when actually it is only a single mismatch.  Image Removed Image Removed
|
CASE STUDIES
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why, despite complete patient HLA, can only a 6/6 but not a 10/10 search report based on haplotype frequency be generated? |
|---|
|
The patient's 5 locus phenotype (10/10) cannot be explained by the haplotypes used for probability matching. The algorithm tries to fall back to 4 locus phenotypes (8/8) and 3 locus phenotypes (6/6). |
- 14:01G covers three), identical (e.g. A*80:01, A*80:01:01 and A*80:01:01G cover exactly the same alleles) or not directly comparable since each code is containing some alleles not covered by the other (e.g. comparing B*07:TDVB and B*07:02:01G the former also covers a lot more variants of B*07:02 like B*07:02:02 to B*07:02:05 while it is excluding other alleles like B*07:44 and B*07:49N).
- The broader code only contains additional alleles which have never been observed in the population whose haplotype frequencies are used - at least not in a relevant haplotypical context. Their frequency could also be so low that it is disregarded due to rounding or the 10% probability grouping explained elsewhere. This applies, in particular, to all null variants of expressed alleles with identical first two field designations.
|
CASE STUDIES
| Expand |
|---|
| title | By default the system should run a 10/10 matched donor run. Why do I get only 8/8 or 6/6 results? |
|---|
| The patient's 5 locus phenotype (10/10) cannot be explained by the haplotypes used for probability matching. The algorithm tries to fall back to 4 locus phenotypes (8/8) and 3 locus phenotypes (6/6).| Why do I get only 8/8 or 6/6 results? |
|
- If the HLA of the patient does not contain information for all 5 loci, the system will automatically scale the match run down to 8/8 or 6/6 depending on the available HLA information of the patient.
|
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why is no probability stated for a highly suitable donor in the haplotype frequency-based a search report? |
|---|
|
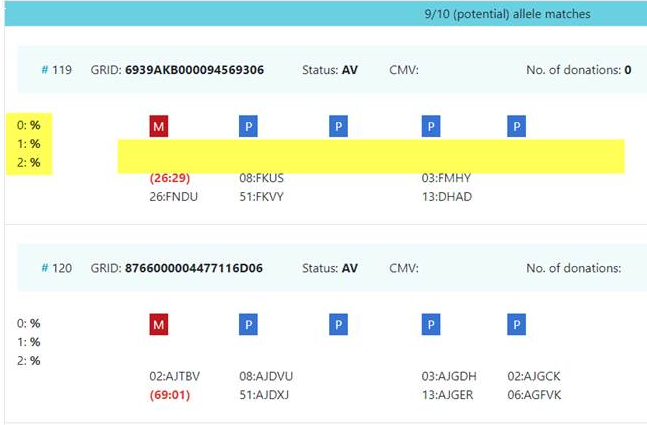 Image Added Image Added
This typically happens for donors when a Most likely, the donor's phenotype cannot be explained by the haplotypes used for probabilistic matching. It is therefore impossible to calculate match probabilities both at the considered loci in total and per-locus. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Why does a DQ mismatch donor not show for my patient under the 8/8 donor list?? |
|---|
|
An Currently, 10/10, 8/8 and 6/6 lists are reserved for donors that have no known mismatches. Donors that have known mismatches for your patients will only be returned when you select "Run a Mismatch Search" and then select to view a 9/10 or 7/8 match type results list.search does not consider DQB1 and therefore will not show whether a donor has or does not have a mismatch for DQB1. If the donor only has a known mismatch at DQB1, this donor will show up in the search results as a potential 8/8 match. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | How does WMDA handle A*02:01 vs *02:03. Antigen =\ or allele =\. Another example is B* 15:01 vs 15:03. |
|---|
|
A*02:01 (2) vs. 02:03 (203) is an allele mismatch because A203 is an associated antigen to A2. B*15:01 (62) vs. B15:03 (72) is an antigen mismatch. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | I performed a cords match run with match type ≥4/6 with class I at antigen level and class II at allele level. Are the probabilities then also determined on this particular match typeAre the calculated probabilities for a CBU search based on antigen level for Class I and allele level for Class II? |
|---|
|
The probabilities shown in your match results table are based on allele level matching and do not correspond with this particular match typeon all loci. |
| Expand |
|---|
| title | If I have a patient with a certain heterozygous locus, how can I ensure that HvG-identical homozygous donors are listed as high up the donor list as possible? |
|---|
|
Currently this feature is not implemented. However, this could be a feature for upcoming versions of the matching program. |
Educational newsletters
No 1: The Sorting order within a donor search report
No 2: Printing of search reports
No 3: New feature added: DPB1 TCE3 model
No 3b: DPB1 TCE3 model update and revised information
...








