...
Abbreviation / column | Description |
| HLA patient | In the grey bar, you can find the HLA of your patient. This header will move with you when you are looking at results more below. |
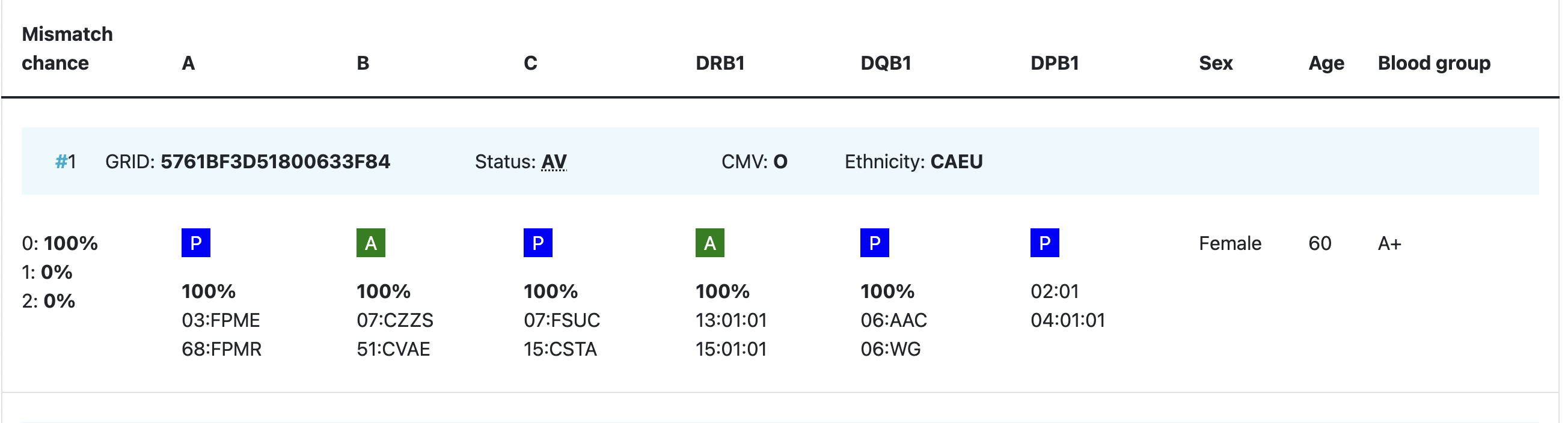
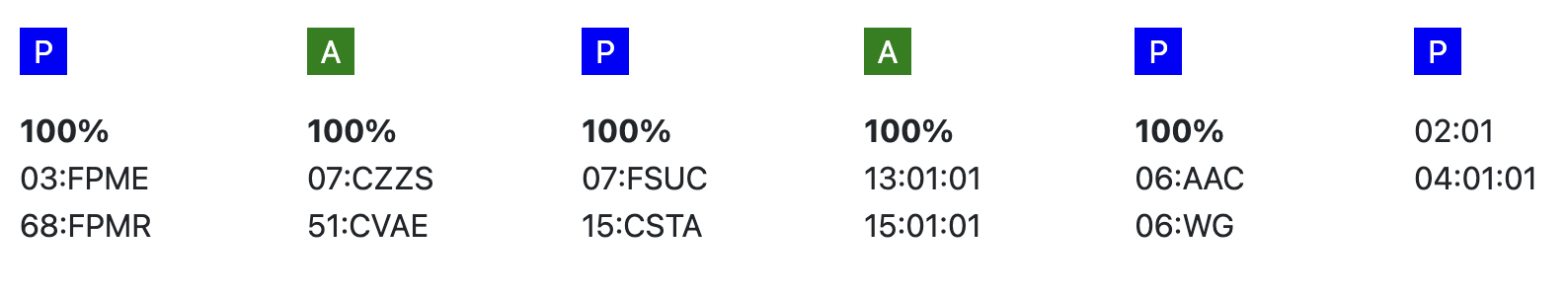
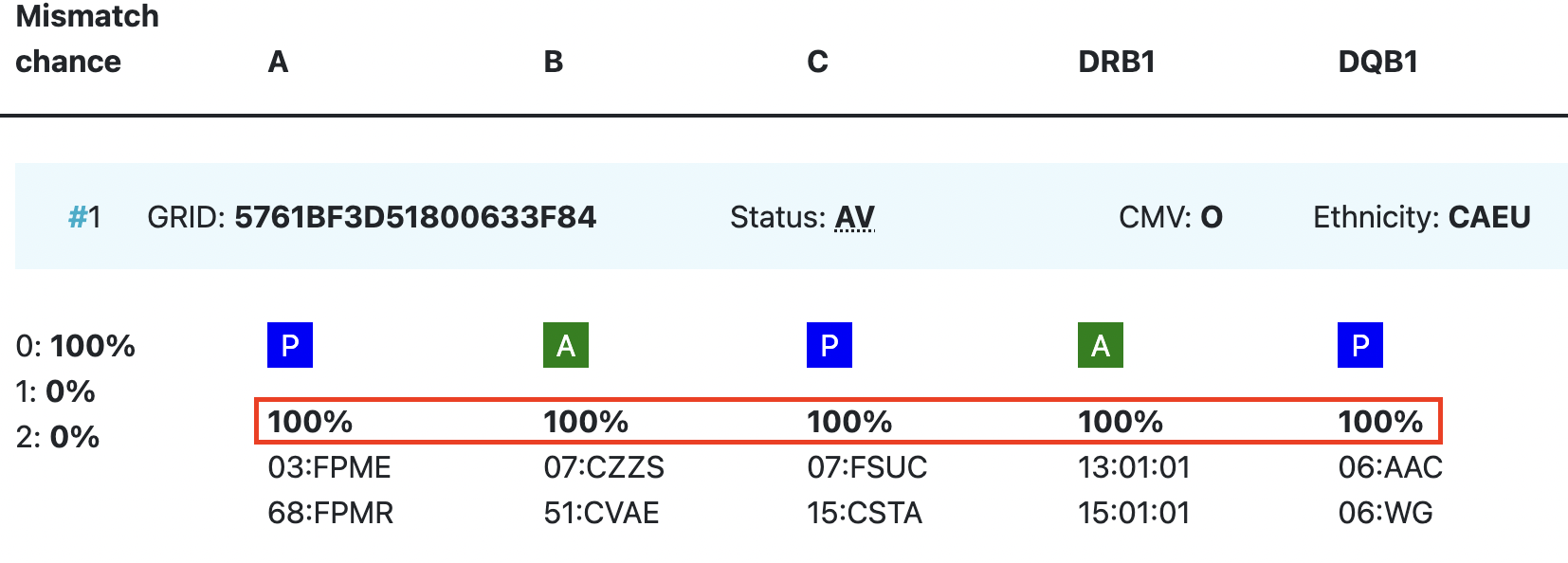
Probability of mismatches 0, 1, 2 | Probability of a mismatch at 0 loci, 1 locus, and 2 loci. The percentages are only shown when you are using the haplotype frequency algorithm and are based on the match type you have been chosen (out of 6 then 6 loci are considered; out of 10 then 10 loci are considered). The five squares above the probability percentages are representing, respectively, locus A, B, C, DRB1, and DQB1. They are showing in letter/colour codes if a certain loci of a donor/cord is likely to match with your patient or not.
NOTE: When you are using for cords the match type ≥4/6 (at HLA-A, B, DRB1), Class I matched at antigen level and Class II matched at allele level, the probabilities are calculated based on allele level match for all loci and not only for DRB1. |
| DPB1 TCE3 grading model | Various studies have shown a potential beneficial effect if the HLA‐DPB1 classification based on T‐Cell Epitopes (TCE) is considered in donor selection. Among the 9/10 and 10/10 donor candidates, those with a permissive DPB1 constellation are preferred over those showing a non‐permissive DPB1 constellation. The implementation in OptiMatch is called "DPB1 TCE3 grading" and is based on the following publications and uses the new score based algorithm that was realised with 3 TCE groups [3].
DPB1 TCE3 evaluation is performed and displayed for
|
Age | Age of donor/cord |
Gender | Sex: M = male, F = female |
Blood group | Blood group, e.g. A+ = blood group A, rhesus positive, B- = blood group B, rhesus negative |
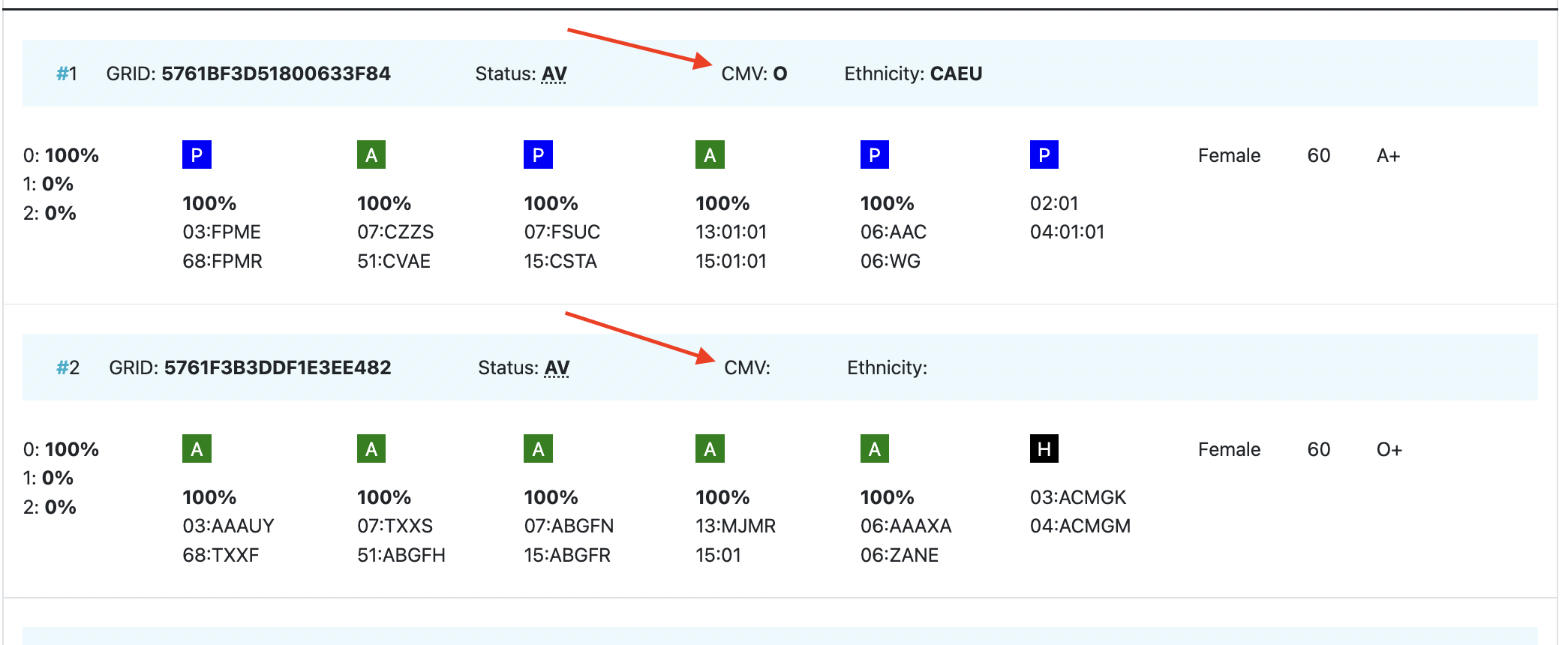
CMV | CMV status Possible values: As seen in the second entry, a value for the CMV status is not required to be entered. |
| Probability of match per locus | If you expand the donor/ cord details, the probability of a match per locus becomes visible: This also correspondents with the letter/colour code from the five squares in the column probability of mismatches. These probabilities are only calculated for the 5 loci A, B, C, DRB1, and DQB1. |
| GRID | GRID, Global Registration Identifier for Donors, is a new ID for donors (not for CBUs) that is globally unique. The first 4 numbers of the GRID refer to the ION of the organisation where the donor is registered. From July 1st 2019, GRID will become the primary ID for communication purposes between organisations. |
Ethnicity | Ethnic group: The system uses the same ethnic groups as defined for the EMDIS system: |
| Status | Status of a donor or CBU. For donors, the status can be available (AV), reserved for a patient (RS), temporarily unavailable (TU) |
...